
The lift coefficient is a relationship between the lift generated by a lifting body to fluid density, fluid velocity, and the associated reference area, this is a dimensionless coefficient. Pitching Moment: The moment or torque produced on the aerofoil by the aerodynamic force is known as the Pitching moment.

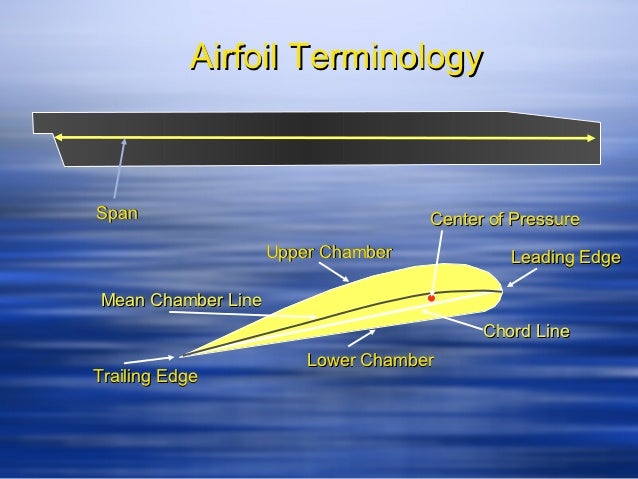
The Angle Of Attack (AOA): The angle of attack is formed between a reference line on a body and the oncoming flow. When the aerofoil is moving through a fluid, the following are the terms used to describe the behaviour:Īerodynamic Center: The centre where the pitching moment is independent of lift coefficient and angle of attack.Ĭenter Of Pressure: The centre where the pitching moment is zero. It is the surface of an aerofoil between the leading and trailing edges, on the upper side. Upper Surface: The upper surface is associated with high velocity and low static pressure, which is also known as suction surface. Trailing Edge: It is an edged part from an aerofoil that hits the air particles last. Maximum Thickness: It is the maximum distance of the lower surface from the upper surface. Maximum Camber: It is the maximum distance of the mean camber line from the chord line. Mean Camber Line: It is a line joining the leading and trailing edges of an aerofoil, at an equal distance from the upper and lower surfaces. It is the surface of an aerofoil between the leading and trailing edges, on the lower side. Lower Surface: The lower surface is a higher static pressure surface which is also known as a pressure surface. Leading-Edge: It is an edged part of an aerofoil that hits the air particles first. It is a distance between the leading and trailing edges measured along the chord line.Ĭhord Line: Chord line is the straight line connecting the leading and trailing edges. The terms which are related to aerofoils are as follows.Ĭhord: Chord can be defined as the distance between the leading edge, at the front of the aerofoil that is the point, and has maximum curvature and the trailing edge, at the rear of the aerofoil, that is the point with a maximum curvature along the chord line. An aerofoil can have many cross-sectional shapes.

An Aerofoil is being designed with a shape that has the capability of producing lift with relatively high efficiency as it passes through the air. To differentiate between different aerofoil shapes, an aerofoil’s properties are defined and specific terminologies are used. Different types of aerofoils are used for the construction of aircraft wings. These are dependent on certain terms that need to be defined to understand the design.Īn aerofoil consists of various cross-sectional shapes. The design of the aerofoil depends on the weight, speed, and purpose of the aircraft and mainly depends on the aerodynamic characteristics. A body that is airfoil-shaped, moving through a fluid produces an aerodynamic force. A similar idea is being used in the designing of hydrofoils which is used when water is used as the working fluid. Lift is the component such that the force is perpendicular to the direction of motion and drag is the component parallel to the direction of motion. Aerofoil is the cross-section design of the wing, blade, or sail. Lift is the component that helps the force turn out to be perpendicular to the motion’s direction while drag is the component that is parallel to the motion’s direction.Īerofoil or also known as Airfoil is a structure with curved surfaces designed to give the most favourable ratio of lift to drag in flight, which is mainly used as the basic form of the fins, wings, and tailplanes of most aircraft. High-speed aircraft mainly implement low-drag, low-lift airfoils that are thin and streamlined and on the other hand, slow aircraft that carry heavy loads use thicker airfoils with high drag and high lift.Īerofoil refers to a cross-sectional shape having a design with a curved surface that provides the most favourable ratio between lift and drag in flight. An aerofoil generates a lifting force that acts at right angles to the airstream and a dragging force that acts in the same direction as the airstream. It is a surface shaped like an airplane wing, tail, or propeller blade, that produces lift and drag when moved through the air.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
